Solar Inverters
Transforming Solar Power for Home Consumption
What does an inverter do?
Solar inverters are an integral part of every solar power system. They perform two key functions:
DC to AC conversion
All solar panels generate Direct Current (DC); a solar inverter is required to convert this into Alternating Current (AC), the form of electricity usable by your home.
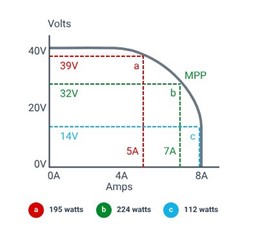
MPP tracking
The operating conditions of solar panels – sunlight intensity and panel temperature – fluctuate throughout the day. This means that the possible solar panel voltage and current are always changing as well. In a process called Maximum Power Point (MPP) tracking, the solar inverter dynamically selects
the exact combination of the two that will produce the most power.
Types of solar inverters
There are two categories to consider when deciding on the right solar inverter type: the solar inverter technology, and the type of solar power system the inverter is for.
Solar inverter technology
String inverter: A string inverter is a single, standalone unit that converts power from a whole string (or strings) of solar panels. String inverters are cheap and convenient, but tend to be the least efficient.
String inverter + power optimizer: Power optimizers are attached to each individual panel. They perform MPP tracking at the module level; the optimized DC power is then sent to the string inverter for conversion into AC power. Combining string inverters with power optimizers will increase your cost but allow your system to handle issues like shading better.
Microinverter: Microinverters are also attached to individual panels. They perform both MPP tracking and power conversion at the module level, allowing each panel to output usable AC power. They’re good at dealing with shade (like power optimizers), and have the additional advantage of making your solar system easy to expand. They are, however, the most expensive type of inverter.
Learn more: Inverter types compared
The type of solar power system the inverter is for
The solar inverter you choose will need to be compatible solar system type you are installing:
1: Grid-tied inverters are meant for grid-tied solar systems, the most common system type. They manage a two-way relationship with the grid, exporting solar power to it, and importing utility power from it as required.
2: Hybrid inverters are designed to work with hybrid solar systems (aka solar-plus-storage systems). They have the same functionality as a grid-tie inverter, but can also charge and draw power from a battery setup.
3: Off-grid inverters are used in off-grid solar systems, i.e. fully independent solar power systems, giving you backup power when the grid is down. An off-grid inverter requires a battery backup to function, and cannot be connected to the grid.
How do solar systems work?
GRID-TIED
Grid-tied solar system
A grid-tied system is the most common type of solar system. It has no solar battery for backup power and utilizes net metering to maximize savings. Solar panels are mounted on your roof then wired together, and the power generated flows into an inverter where direct current (DC) electricity is converted into alternating current (AC) electricity. This electricity is either used by your home or is exported to the utility grid.
HYBRID
Hybrid solar system
In hybrid solar systems, rooftop solar panels are connected to both a solar battery and the electric grid. The solar electricity generated by your panels that your home does not use is stored in the battery instead of being sent to the grid, which reduces your reliance on the utility while also providing backup power when needed. Battery storage is still expensive but you may be able to reduce costs by using government incentives.
OFF-GRID
Off-grid solar system
Off-grid solar systems are not connected to the grid at all, so all of your energy needs must be met by the sun. There is no utility to fall back on. The solar installation needs to power your home not only during the day but after dark as well, so many solar panels and a large battery system are required. These systems are often expensive and don’t make sense for homes that have access to the grid.
